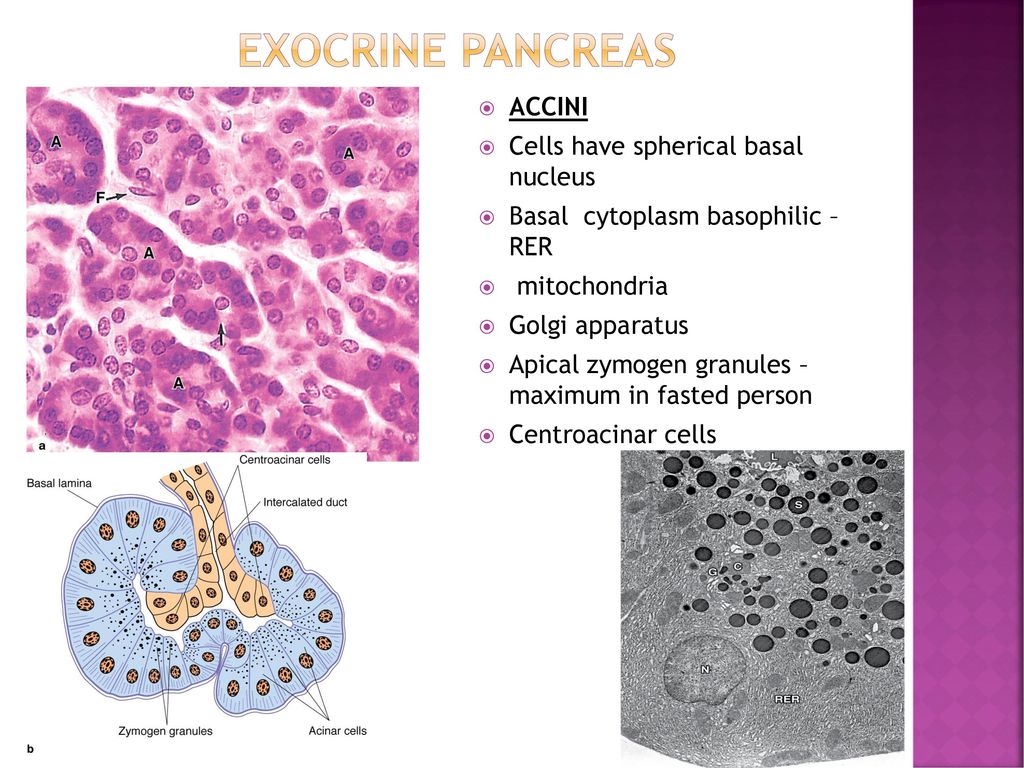
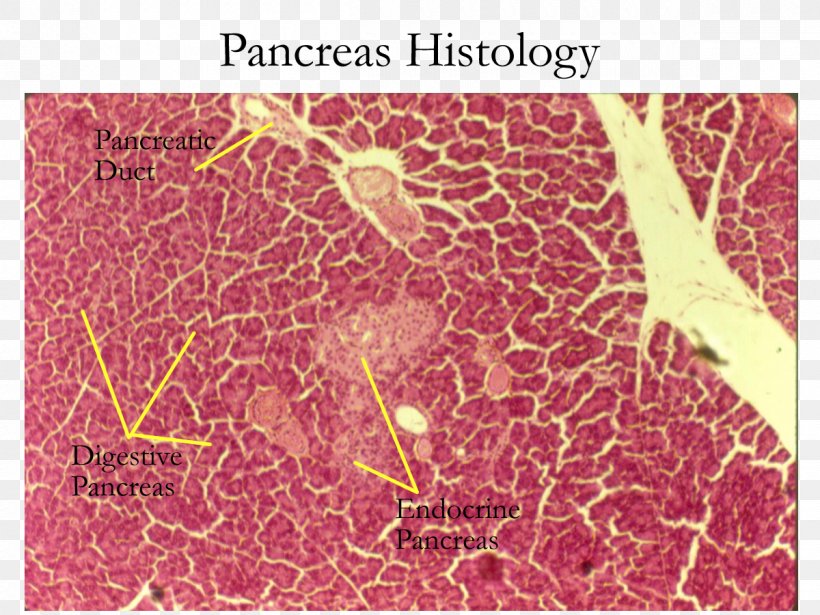
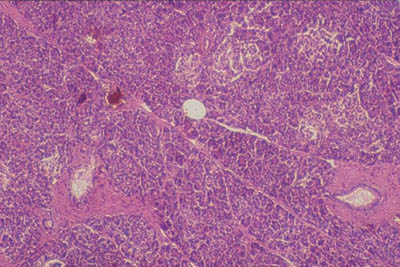
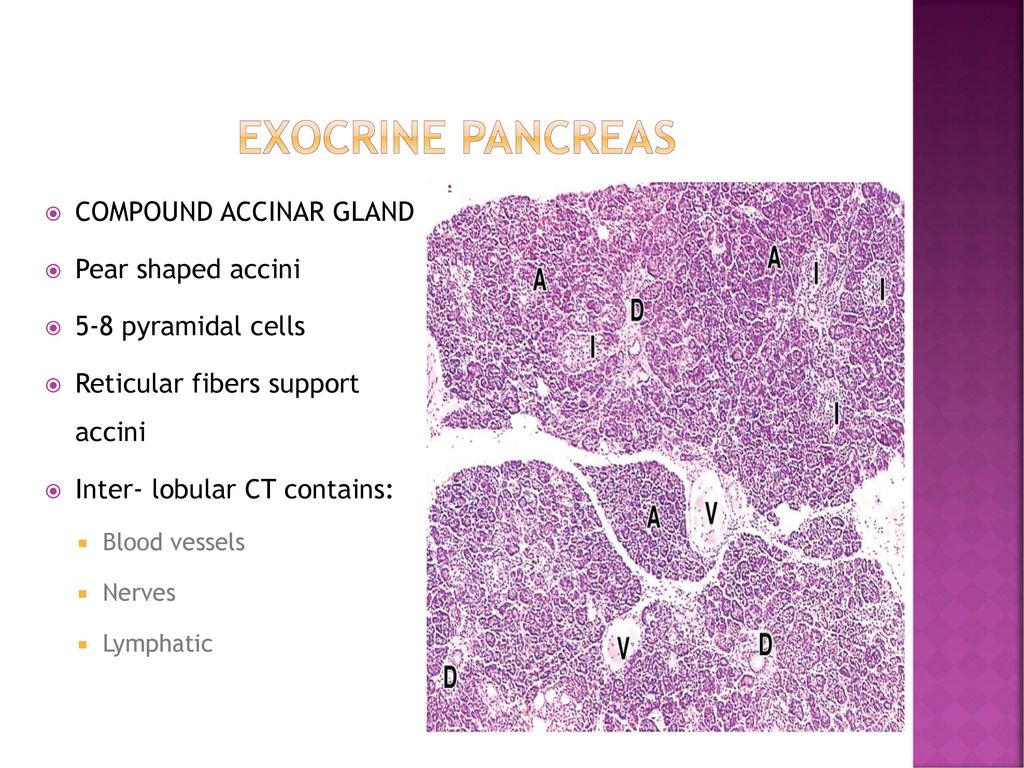
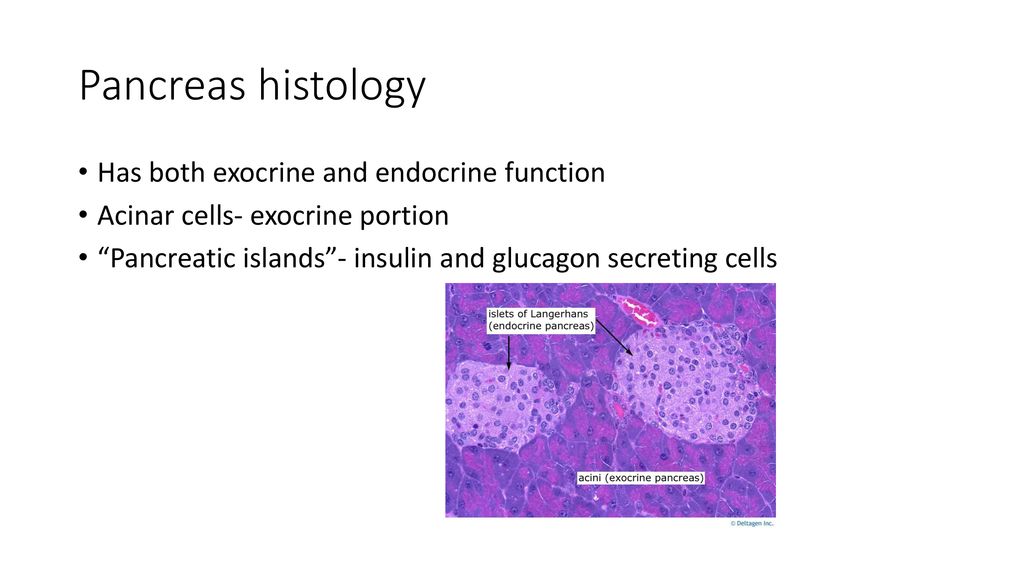
The exocrine secretory part consists of serous acini (known as pancreatic acini), whereas the islets of Langerhans form the endocrine part The major part of pancreas corresponds to the exocrine part (99 % in humans) The serous exocrine cells show a rounded nucleus and dark cytoplasmPancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue The pancreas is surrounded by a very thin connective tissue capsule that invaginates into the gland to form septae, which serve as scaffolding for large blood vessels Further, these septae divide the pancreas into distinctive lobules, as can clearly be seen in the image of mouse pancreas below (H&E)An essential pancreatic function is the conversion of food into fuel for the body's cells The exocrine part produces mainly digestive enzymes and helps in digestion, whereas the endocrine part is responsible for the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism (ie blood
Endocrine Pancreas
Exocrine vs endocrine pancreas histology
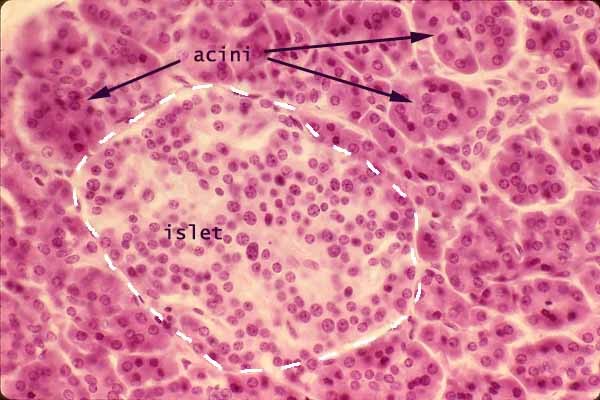
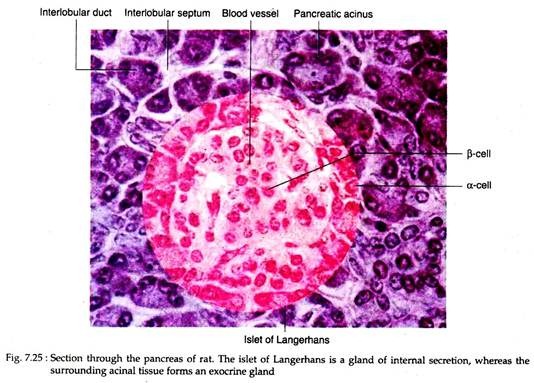
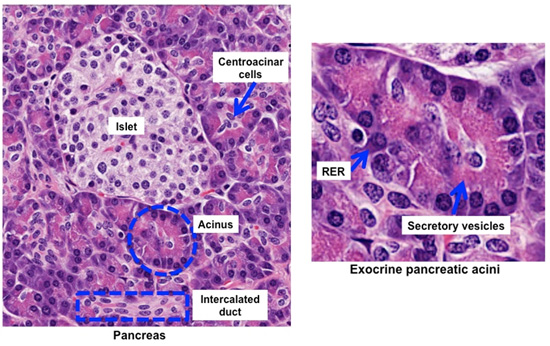
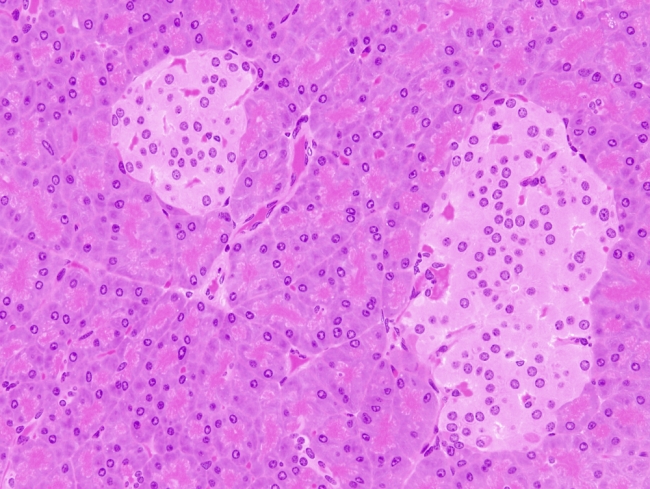
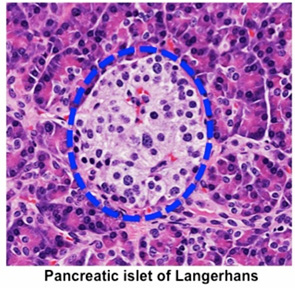
Exocrine vs endocrine pancreas histology-Pancreatic Histology Endocrine Tissue If you examine a section of pancreas at low magnification, you will undoubtedly observe distinctive areas of pale staining embedded within the exocrine tissue of lobules (marked with a red * below) These are the Islets of Langerhans, the endocrine component of the pancreasThe endocrine pancreatic tissue consists of small, discrete clusters of cells, called islets of Langerhans (also called pancreatic islets), scattered throughout the exocrine pancreatic lobules Unlike the exocrine pancreatic acini, which secrete into a ductular system, cells of the islets of Langerhans secrete directly into small fenestrated capillaries that are integrated within
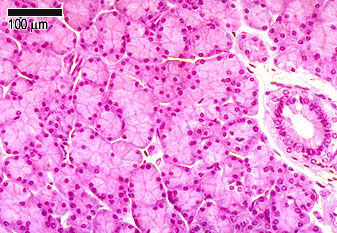



Glandular Tissue The Histology Guide
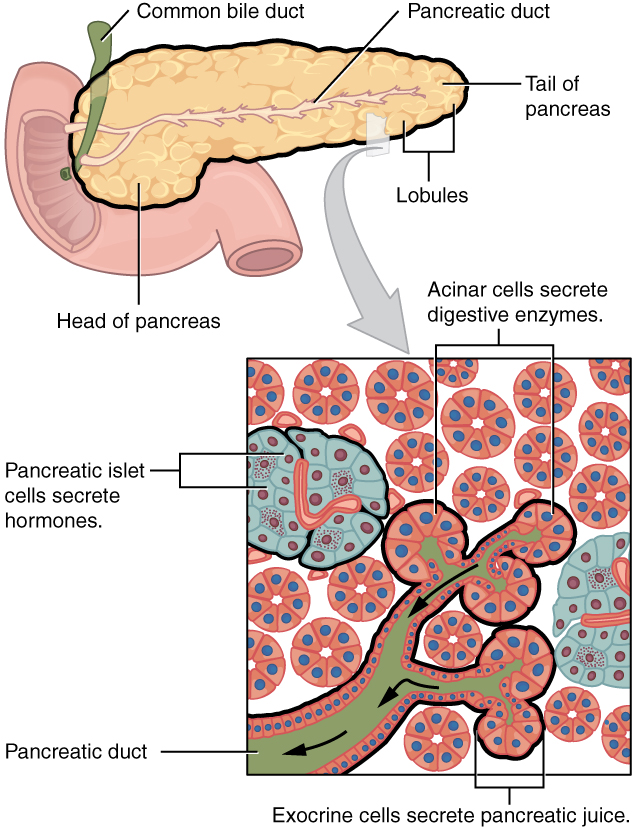
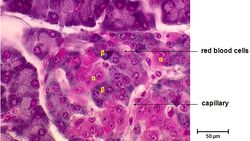
Up to10%cash backThe exocrine secretion products are collected and delivered by a duct system which is drained by the pancreatic ducts The endocrine component is composed of small clumps of cells, named the islets of Langerhans, which are scattered throughout the exocrine glandular tissue The history of the endocrine pancreas has been recently reviewed (S amols230 Pancreas Endocrine Pancreas View Virtual EM Slide You will not be ask to identify different types of endocrine cells in the islet of Langerhans However, compare the appearance of an endocrine cell containing small granules to that of a portion of exocrine cell shown on the rightThe endocrine component of the pancreas consists of the islets of Langerhans, the round masses of glandular epithelial cells appearing as nodules in the endocrine pancreas The cells are found in irregular cords and clumps, as opposed to the neighboring, highly organized acini of the exocrine pancreas They are surrounded by a network of capillaries
The morphology of the exocrine secretory unit of the pancreas, ie the pancreatic acinus, is reviewed The histological features of the acini and their relation with the duct system are described The acinar three‐dimensional architecture was studied by means of different ultrastructural techniques, some of which are complementaryExocrineArranged as pancreatic acinar cellsProduct released into ductal systemSecretions=zymogens and bicarbonate EndocrineArranged as islets of LangerhansProduct released into bloodSecretions=hormonesExocrinereleases enzymes aiding in digestion Endocrine pancreascomponents produced by islets>bloodstream
The pancreas is both an exocrine accessory digestive organ and a hormone secreting endocrine gland The bulk of the pancreatic tissue is formed by the exocrine component, which consists of many serous pancreatic acini cells These acini synthesize and secrete a variety of enzymes essential to successfully "rest and digest"Exocrine part of the pancreas Histologically, the exocrine part of the pancreas shows the typical structure of the serous gland and represents roughly 98% of the organ's tissue The acini consist of strong basophilic cells, which contain numerous secretory granules Acini are made of zymogenic cells that surround a central lumen and are arranged in lobulesThe pancreas is both an exocrine and an endocrine gland The endocrine pancreas consists of accumulations of palestaining cells called islets of Langerhans, which are surrounded by pancreatic acini The islet is composed of different populations of cells that secrete insulin, glucagon, somatostatin or pancreatic polypeptide




Pancreas Objectives The Student Should Be Able To Describe 1 The Endocrine Part Of The Pancreas Within The Exocrine Part 2 The Histological Features Ppt Download



Pituitary Gland
Some glands retain their continuity with the surface via a duct and are known as EXOCRINE GLANDS Other glands lose this direct continuity with the surface when their ducts degenerate during development These glands are known as ENDOCRINE glands show labels This is the parotid gland, a type of salivary glandUp to10%cash backThe exocrine secretion products are collected and delivered by a duct system which is drained by the pancreatic ducts The endocrine component is composed of small clumps of cells, named the islets of Langerhans, which are scattered throughout the exocrine glandular tissue The history of the endocrine pancreas has been recently reviewed (SamolsA brief review of the normal histology of the pancreas, as presented by the URMC Pathology IT Program




Pancreas Histology




Pancreas Histology
Exocrine vs Endocrine Fundamentally, the difference between exocrine and endocrine is exocrine secretes (via ducts) to an external surface or body cavity endocrine secretes within an enclosed system eg the bloodstream As the acini of the pancreas secrete into a network of ducts, this gives this organ an exocrine function



Chapter 15 Page 7 Histologyolm 4 0
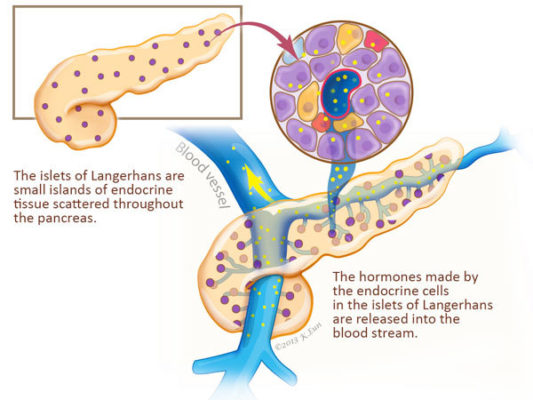



Pancreas Function Pancreatic Cancer Johns Hopkins Pathology




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
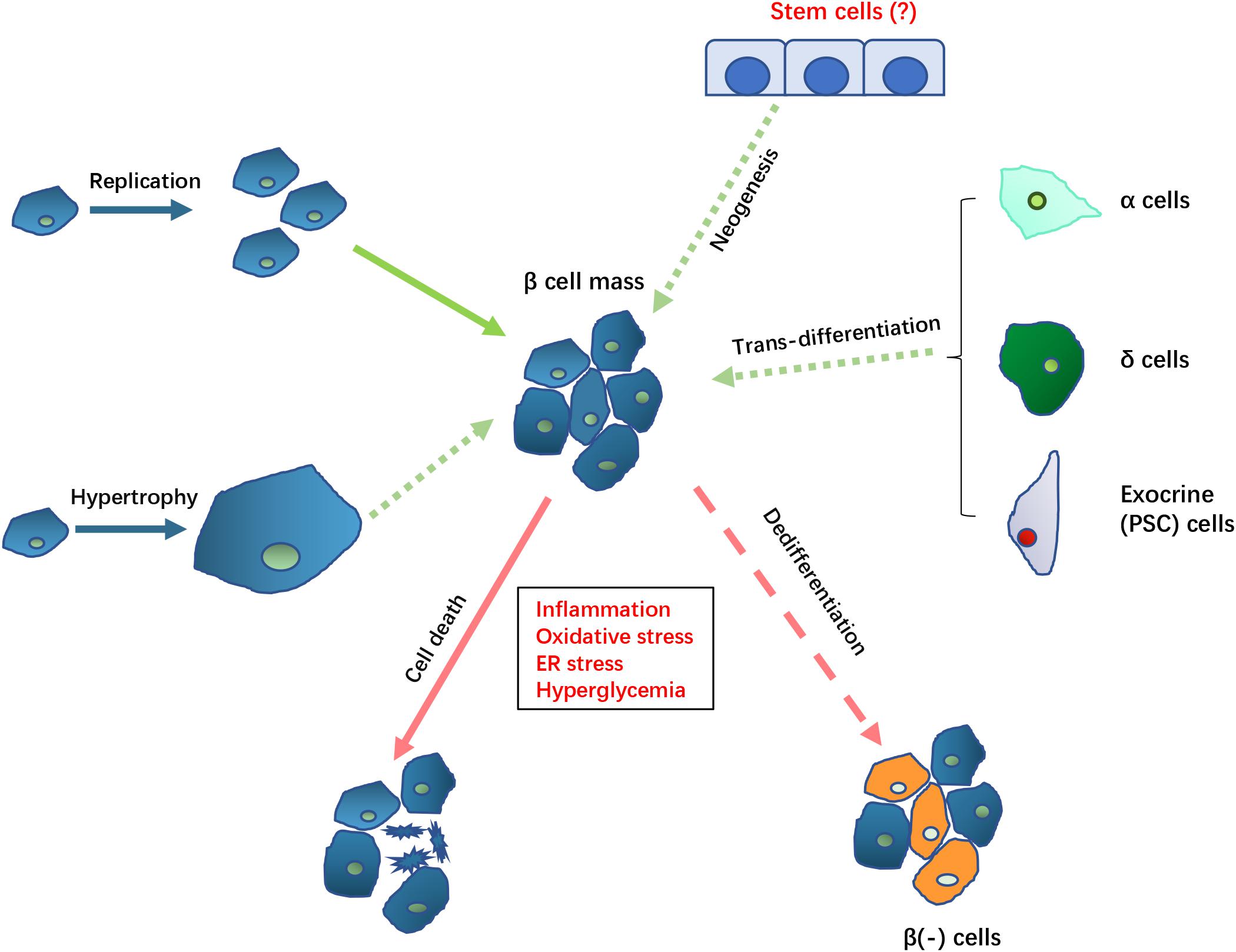



Frontiers Pathological Mechanisms In Diabetes Of The Exocrine Pancreas What S Known And What S To Know Physiology
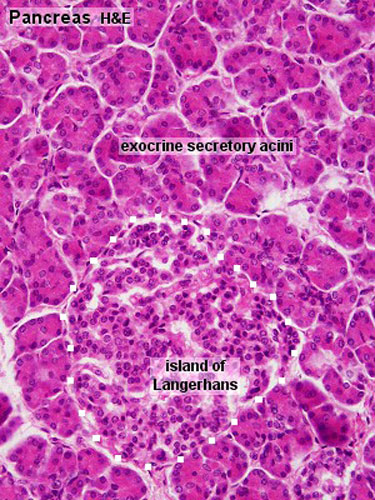



Gastrointestinal Tract Pancreas Histology Embryology




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia




Pancreatic Histology At The End Of Experimental Period Endocrine Download Scientific Diagram




Pancreas Wikipedia



Histology Of Pancreas Ppt Download




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia




Men1 Maintains Exocrine Pancreas Homeostasis In Response To Inflammation And Oncogenic Stress Pnas



Histology At Siu




Histoquarterly Pancreas Histology Blog
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1059/SXYoNKo9I26Aroj0YPbuHg_pancreatic-duct-system_english.jpg)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub
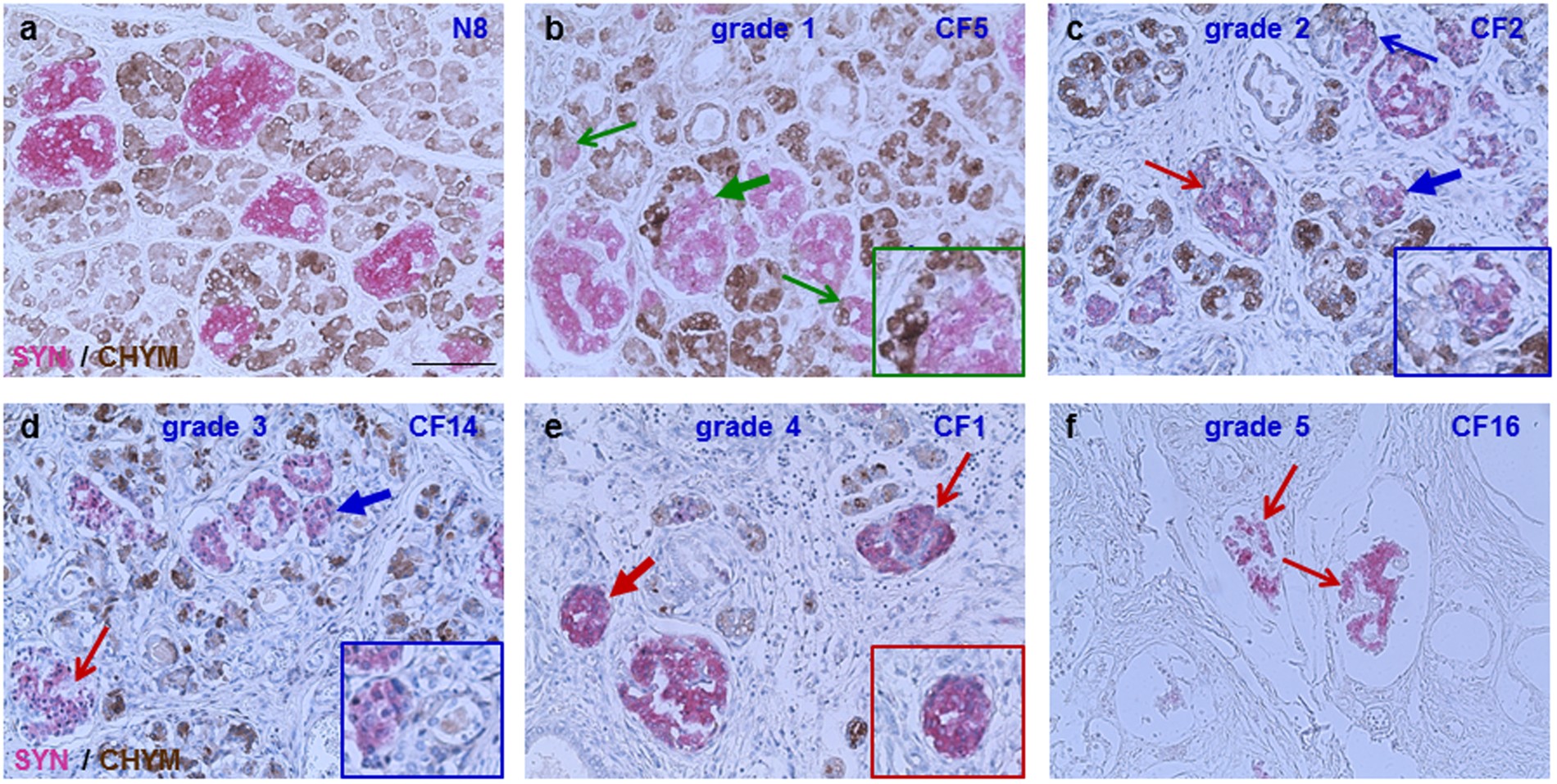



Structural Abnormalities In Islets From Very Young Children With Cystic Fibrosis May Contribute To Cystic Fibrosis Related Diabetes Scientific Reports




Pancreas Histology Osmosis




Comparison Of Marmoset And Human Endocrine And Exocrine Pancreatic Download Scientific Diagram




Pancreas Histology Draw It To Know It



Pathology Outlines Anatomy Histology
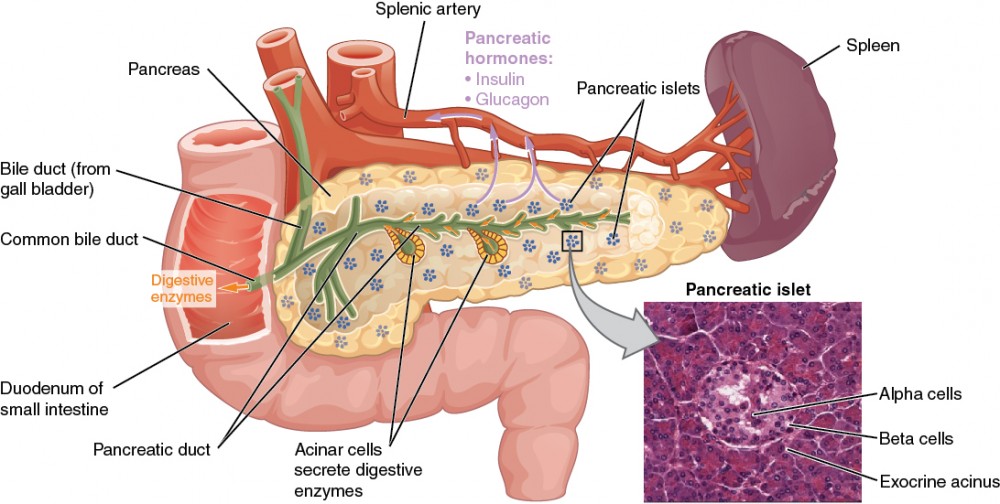



The Endocrine Pancreas Anatomy And Physiology Ii



Exocrine Gland Pancreas Histology Endocrine Gland Endocrine System Png 10x900px Watercolor Cartoon Flower Frame Heart Download




Pancreatic Islets Wikipedia




Pancreas Histology Flashcards Quizlet




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia



Digestive The Histology Guide




Pancreas Histology Pancreas Labels Histology Slide Medical School Studying Histology Slides Medical Education
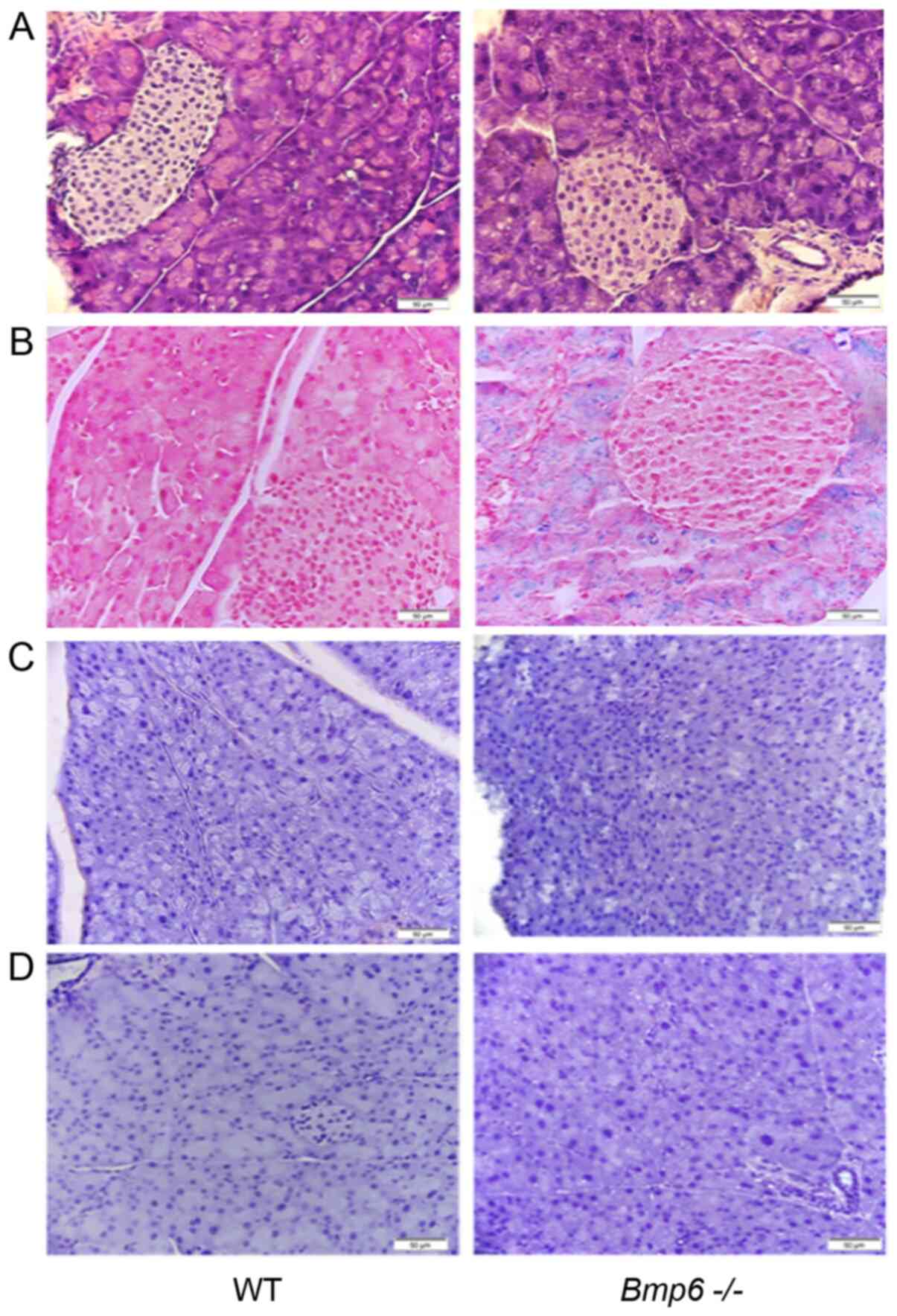



Iron Overload In Aging Em Bmp6 Sup Sup Em Mice Induces Exocrine Pancreatic Injury And Fibrosis Due To Acinar Cell Loss




Human Pancreatic Afferent And Efferent Nerves Mapping And 3 D Illustration Of Exocrine Endocrine And Adipose Innervation American Journal Of Physiology Gastrointestinal And Liver Physiology



Pancreas Histology Coyar




Jci Abnormal Endocrine Pancreas Function At Birth In Cystic Fibrosis Ferrets
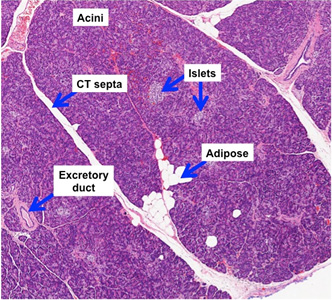



Human Structure Virtual Microscopy




Pancreatic Tumors Vca Animal Hospital



Labeled




Pancreas Sciencedirect




Glandular Tissue The Histology Guide




Pancreas



Pancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue



Pancreas Development Location And Hormones Human




Histology Of Mouse Pancreas Stained By Hematoxylin Eosin Normal Download Scientific Diagram
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1881/CPsIC67xuz6pLt6JhAM6Wg_pancreas-histology_english.jpg)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub



Endocrine Pancreas



Histology World Histology Fact Sheet Pancreas
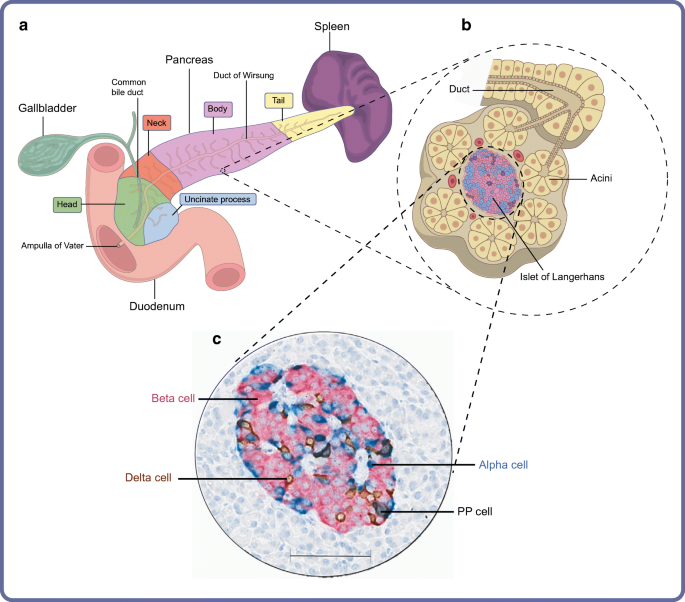



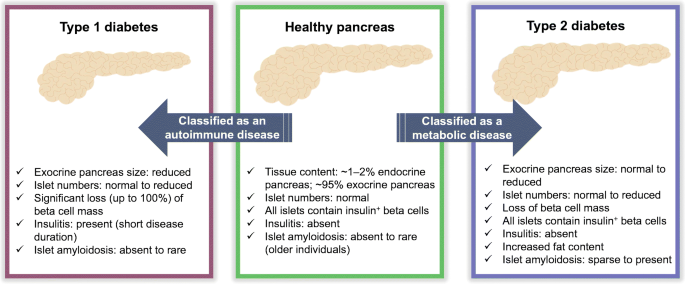
Organisation Of The Human Pancreas In Health And In Diabetes Springerlink



Pancreatic Histology Endocrine Tissue




Histoquarterly Pancreas Histology Blog




Pancreas Sciencedirect



2




Endocrine System 1 Overview Of The Endocrine System And Hormones Nursing Times



Ha 235 Histology Accessory Digestive Glands
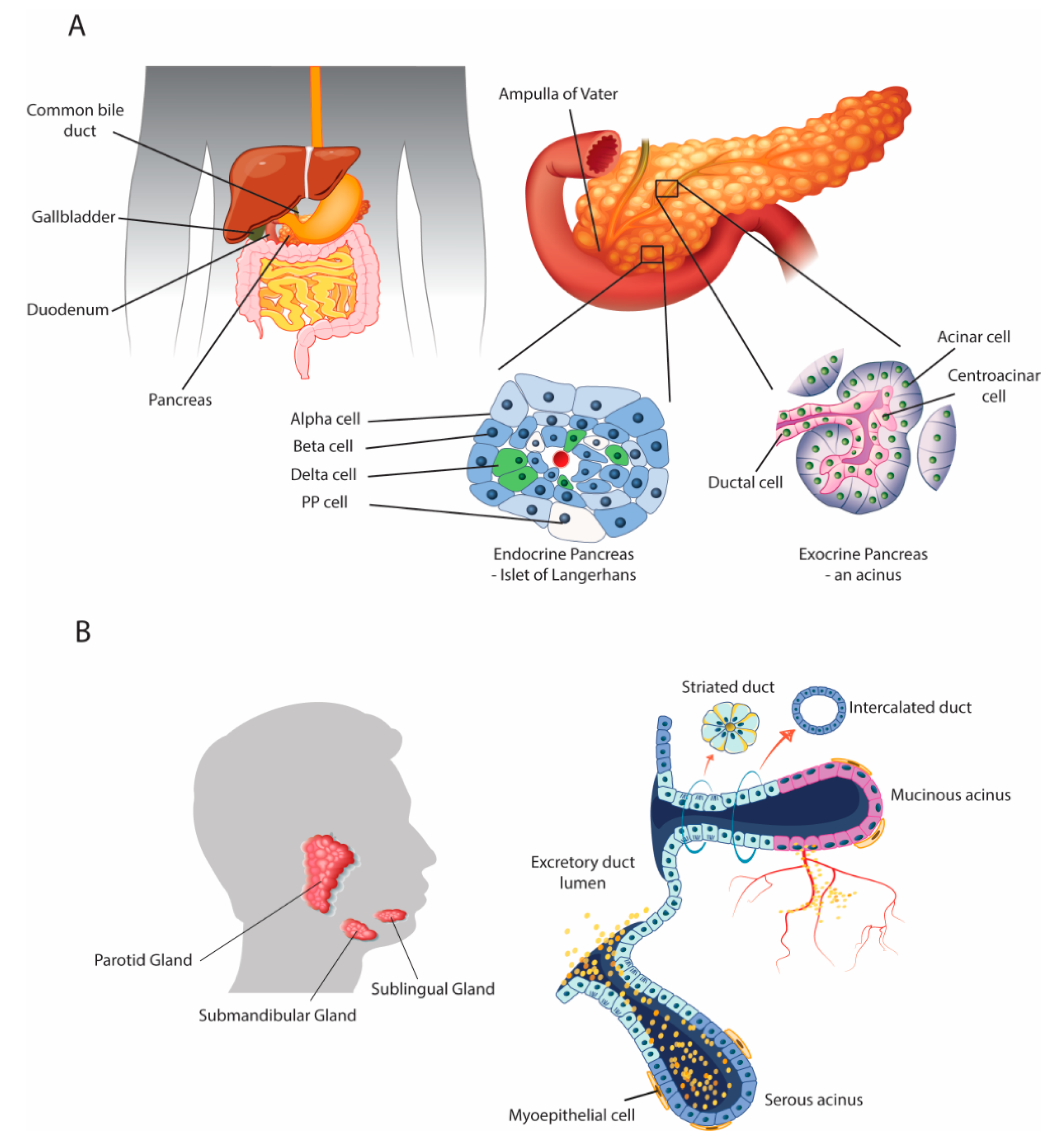



Biomedicines Free Full Text Defining Parallels Between The Salivary Glands And Pancreas To Better Understand Pancreatic Carcinogenesis Html



Liver And Pancreas



Endocrine System Pns



1



Pancreas Histology Coyar




Pathology Of The Exocrine Pancreas Tyler Verdun Pgy



Functional Anatomy Of The Endocrine Pancreas



Histology Of Pancreas Ppt Download



2
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/pancreatic-acini/M2LWbCSc8l4TbZ24lNYg_Pancreatic_acinus.png)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub




Exocrine Pancreas Sciencedirect



Pancreas Endocrine And Exocrine Functions Medical Library




Histology Endocrine Glands Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Dictionary Normal Pancreas The Human Protein Atlas



Human Structure Virtual Microscopy



Pancreas Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English




Endocrine



Animal Tissues Epithelium Pancreas Exocrine And Endocrine Gland Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology



Histology Of Three Endocrine Glands Ppt Download
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/body-of-pancreas-3/mbuhIx2qC3HVaYNH69w_Body_of_Pancreas.png)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub



Human Structure Virtual Microscopy



Ha 235 Histology Accessory Digestive Glands




Histology Of Pancreas Youtube



Organisation Of The Human Pancreas In Health And In Diabetes Springerlink
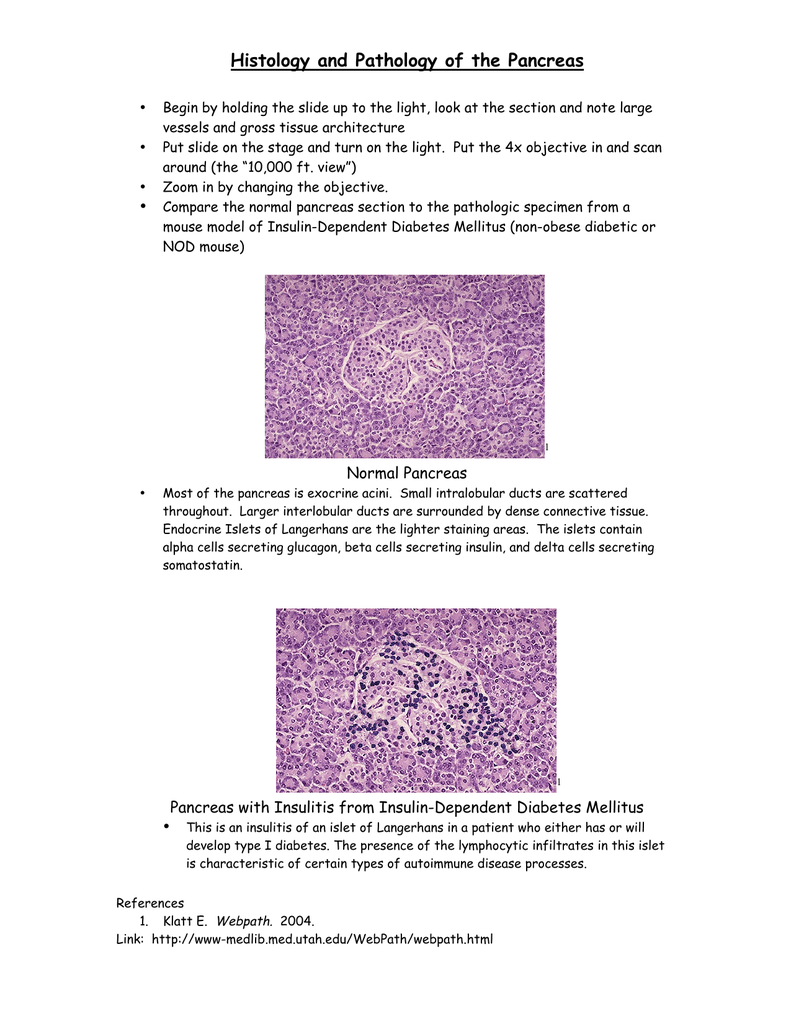



Histology And Pathology Of The Pancreas



Normal Pancreas Pancreas Org




Exocrine Pancreas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Pathology Of The Exocrine Pancreas Flashcards Quizlet




Pathology Of The Exocrine Pancreas Tyler Verdun Pgy



1



Histology Home Page
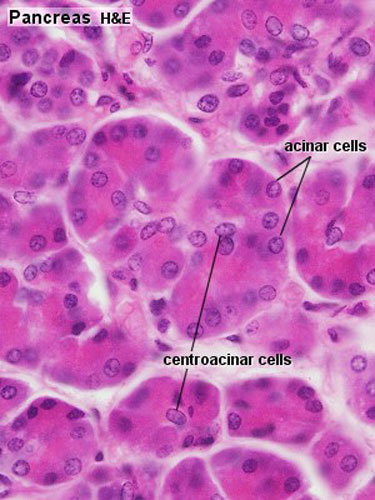



File Pancreas Histology 002 Jpg Embryology




Pancreas Histology Flashcards Quizlet




Histological Images Of The Pancreas Note That The Noticeable Decrease Download Scientific Diagram




Pancreas Wikipedia
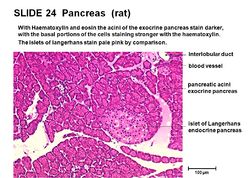



Pancreas Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
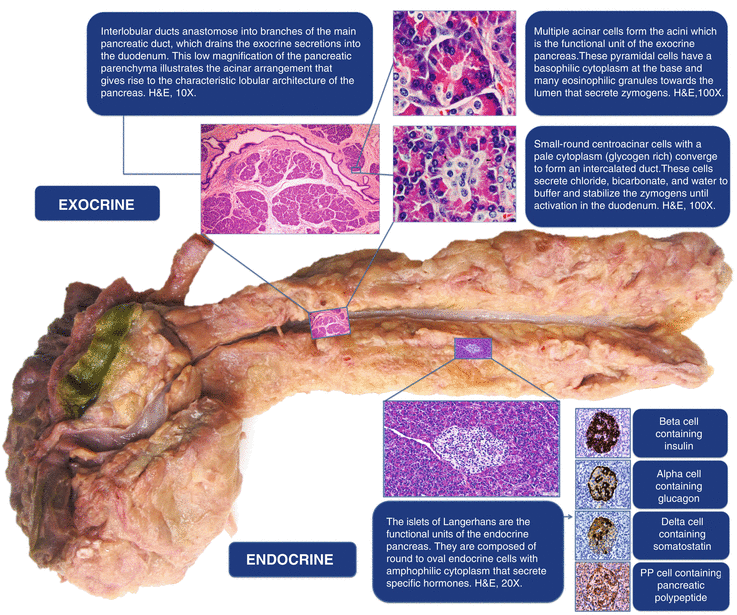



Histology Of The Pancreas Radiology Key
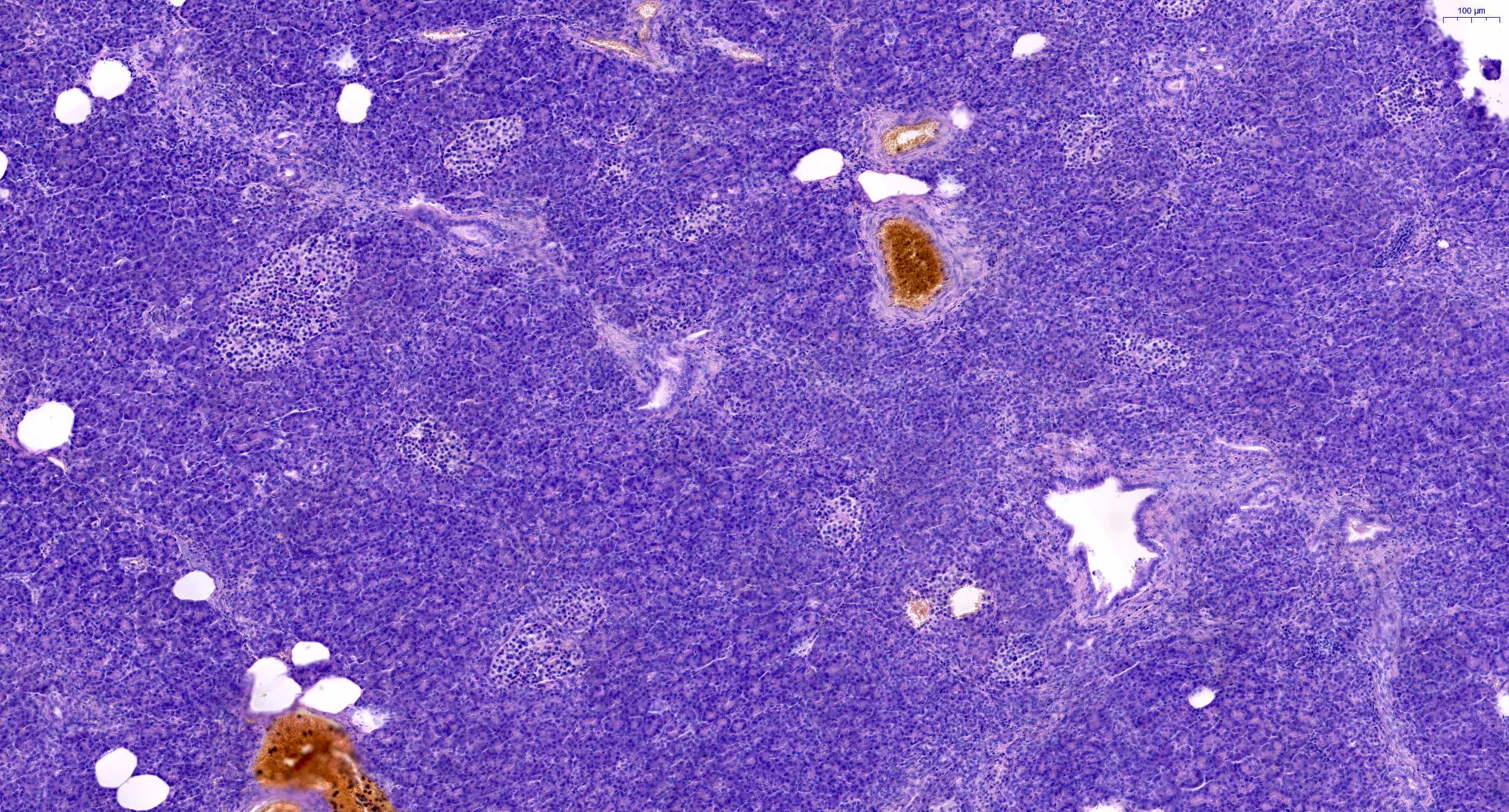



Pathology Outlines Anatomy Histology




Histology Of The Pancreas Endocrine And Exocrine Youtube




Histoquarterly Pancreas Histology Blog



Endocrine System Pns




A Tale Of Two Pancreases Exocrine Pathology And Endocrine Dysfunction Abstract Europe Pmc




Pdf Histology Of Endocrine Pancreas In The Chabro Chicken Semantic Scholar




Picture Test In Histology Of The Endocrine Glands Youtube



Liver And Pancreas



Chapter 15 Page 7 Histologyolm 4 0




Endocrine Pancreas Development In Growth Retarded Human Fetuses Diabetes
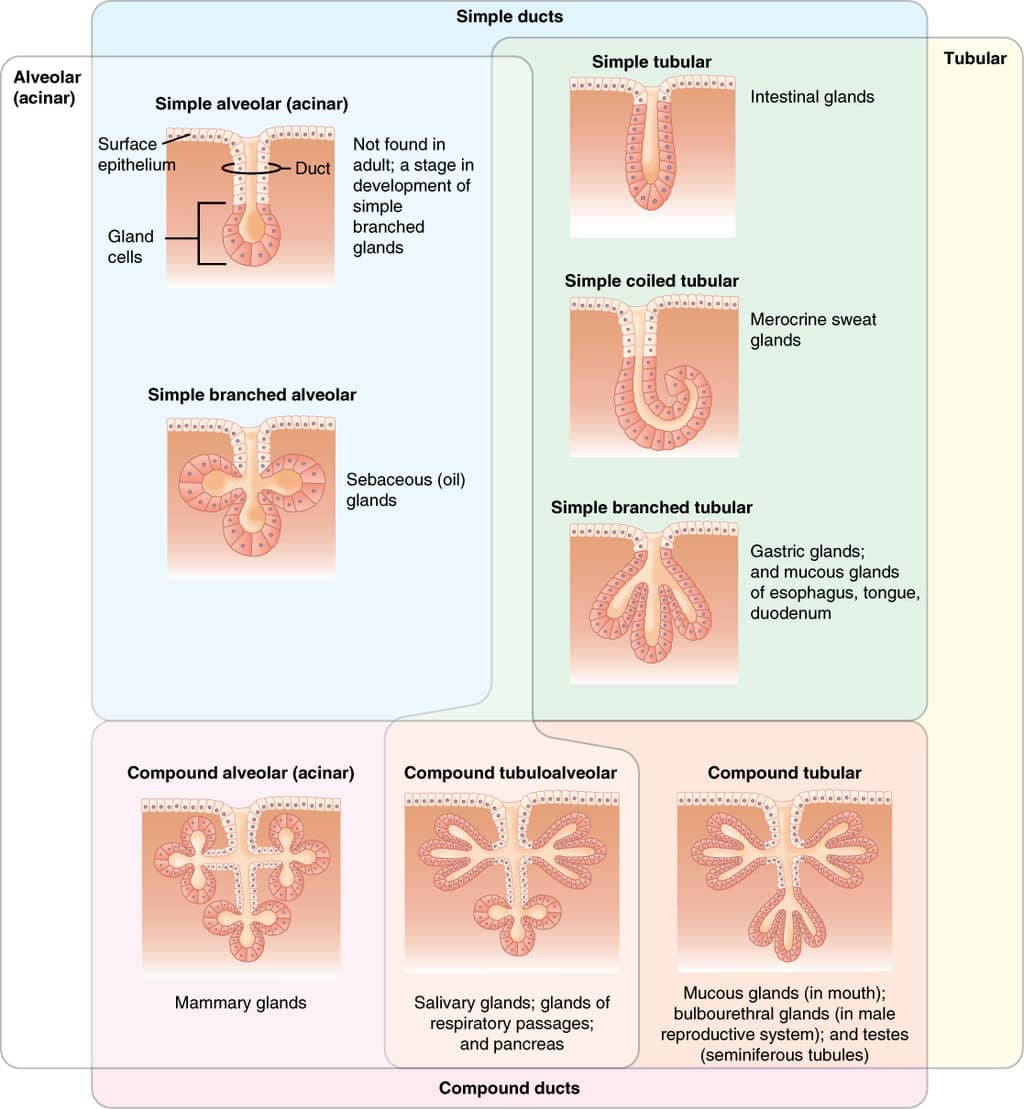



Structure Of Glands Exocrine Endocrine Histology Teachmephysiology



Pancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue



Pancreatic Histology Endocrine Tissue




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿